| Newsletter Italian February/March 2022 |

|

|



ICRANet Newsletter
2014 -
2015 -
2016
2017 - 2018 - 2019 2020 - 2021 2022 February/March - April/May/June - July/August/September - October/November - December/January 2023 2023
ICRANet Newsletter
Febbraio/Marzo 2022
SOMMARIO
1. Comunicato stampa ICRA - ICRANet - CONICET - UNLP "One star could finally reveal the nature of what does lie at the Milky Way center" 2. GCN pubblicata da ICRANet, 25 Febbraio 2022 3. Annuncio importante: 80esimo compleanno del Prof. Remo Ruffini (Nizza, 16 - 18 Maggio 2022) e 6° Bego Meeting Summer School (Nizza, 4 - 14 Luglio 2022) 4. Visita di S.E. Tsovinar Hambardzumyan, Ambasciatrice dell'Armenia in Italia, presso il centro ICRANet di Pescara, 16 Marzo 2022 5. Nuovo accordo di cooperazione tra l'ICRANet e la University of Western Cape (UWC), 1 Marzo 2022 6. Nuovo accordo di cooperazione tra l'ICRANet e la Sogang University, 28 Marzo 2022 7. Rinnovo dell'accordo di cooperazione tra l'ICRANet e l'Institute of High Energy Physics presso l'Accademia Cinese delle Scienze (IHEP CAS), 7 Marzo 2022 8. Podcast del Prof. Remo Ruffini "20 Marzo 1916: Einstein pubblica la Teoria Generale della relatività", Radio Storia La Repubblica, 20 Marzo 2022 9. Pubblicazioni Recenti
1. Comunicato stampa ICRA - ICRANet - CONICET - UNLP "One star could finally reveal the nature of what does lie at the Milky Way center"
A new study deepens on the nature of the compact object sitting at our Galaxy center, SgrA*, by analyzing the astrometric data of one of the closest and long-studied stars that orbit around it. The international team of researchers from ICRA-ICRANet and CONICET-UNLP has found that besides the traditional black hole (BH) hypothesis, a dense concentration of dark matter (DM) made of fermions (called darkinos) can explain the detailed data (positions and velocities) of the star S2. The work provides a way to distinguish observationally between these two scenarios using the precession of the S2 orbit, very much in the same way that the theory of general relativity was proven using the precession of Mercury's orbit around the Sun. This new article, published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Letters1, holds relevant implications about the nature and mass of the dark matter particles.
For about three decades, two independent observational campaigns have monitored a cluster of young and bright stars orbiting the central parsec of our Galaxy to constrain the mass and nature of the massive object harbored at the center. These precise and accurate measurements have been possible thanks to the most powerful telescopes on earth. This achievement led to the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2020 awarded to Reinhard Genzel and Andrea Ghez: for the discovery of a supermassive compact object at the center of our galaxy. Traditionally, a classical BH has been the most accepted hypothesis for the nature of SgrA*. The reason for this is that the orbits of the few detected S-stars are nearly perfect ellipses, implying the existence of a very compact object placed at its focus. Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that the orbits cannot be Keplerian because there is a precession of the periapsis. The new work demonstrates that this effect is also present in the case of the DM core model and that its entity agrees with all publicly available data that shows the existence of this relativistic pattern in the S2 orbit. The article predicts that the two scenarios on the nature of SgrA* could be discriminated by measuring the precession of S2 around the next apocenter passage that will occur in 2026. The reason behind this difference is that while the BH predicts a unique prograde precession, in the DM scenario, it can be either retrograde or prograde, depending on the amount of DM filling the orbit, which depends on the mass of the darkinos. A remarkable aspect of this novel DM interpretation of SgrA* is that the DM distribution is not constrained to the core of the Galaxy. The DM configuration extends to the outskirts of the Galaxy, forming a dilute halo that explains the circular velocity of far away objects as welll!. This result, together with a related study (see https://twitter.com/RAS_Journals/status/1489539729037008899?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw) obtained by some of the research team, hints towards a paradigm shift in the field of DM halos and supermassive BH formation. It suggests that non-active galaxies as our own host dense DM concentrations at their centers, while more massive and active-galaxies, host supermassive BHs that has been formed from the gravitational collapse of these DM cores. 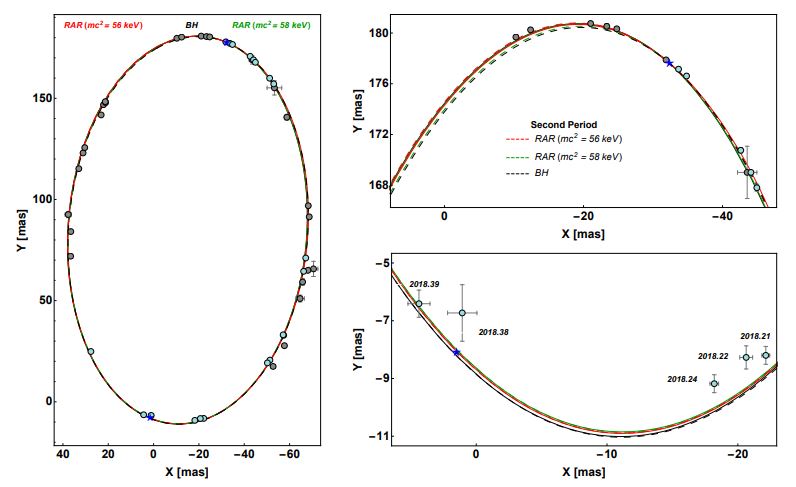
FIG. 1. Figure taken from [1] with the kind permission of the authors. Relativistic precession of S2 in the projected orbit on the plane of the sky as predicted in the BH and RAR DM models. While it is prograde for the BH and RAR (m = 58 keV/c2) (in dashed black and green respectively), it is retrograde for the RAR DM model (m = 56 keV/c2) (in dashed red). The solid (theoretical) curves and gray (data) points correspond to the first period (≈ 1994-2010) while the dashed (theoretical) curves and cyan (data) points to the second period (≈ 2010-2026). Right panels: zoom of the region around apocentre (top panel) and pericentre (bottom panel). The astrometric measurements are taken from Do et al.2. 
FIG. 2. Relativistic precession of S2 as manifested in the right ascension as a function of time after last pericentre passage, where effects are more prominent. BH model (Left panel) and RAR model for m = 56 keV/c2 (Right panel). Comunicato stampa sul sito dell'ICRANet: http://www.icranet.org/communication/ Comunicato stampa sul sito di Oxford University Press: https://oxfordjournals.altmetric.com/details/113891044 Comunicato stampa sul sito Conicet-Argentina: https://laplata.conicet.gov.ar/un-nuevo-paso-para-desentranar-que-hay-en-el-centro-de-la-via-lactea/ Upcoming S2-star astrometry could potentially establish if SgrA* is governed by a classical BH or by a quantum DM system: read more in a paper just published in MNRAS (Argüelles et al) at https://t.co/Wbx3kSMokD . #SagittariusA* #darkmatter #darkinos #fermions #blackholes pic.twitter.com/lWMz7d5l8D — RAS Journals (@RAS_Journals) February 4, 2022
------------
1 C. R. Argüelles, M. F. Mestre, E. A. Becerra-Vergara, V. Crespi, A. Krut, J. A. Rueda, and R. Ruffini, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters 511, L35 (2021), arXiv:2109.10729, URL https://doi.org/10.1093/mnrasl/slab126. 2 T. Do, A. Hees, A. Ghez, G. D. Martinez, D. S. Chu, S. Jia, S. Sakai, J. R. Lu, A. K. Gautam, K. K. O'Neil, et al., Science 365, 664 (2019), 1907.10731.
2. GCN pubblicata dall'ICRANet, 25 Febbraio 2022
TITLE: GCN CIRCULAR
NUMBER: 31648 SUBJECT: GRB 220101A: The first example of a Petanova DATE: 22/02/25 11:38:50 GMT FROM: Remo Ruffini at ICRA ruffini@icra.it R. Ruffini, Y. Aimuratov, L. Becerra, C.L. Bianco, Y-C. Chen, C. Cherubini, Y.F. Cai, S. Eslamzadeh, S. Filippi, M. Karlica, Liang Li, G.J. Mathews, R. Moradi, M. Muccino, G.B, Pisani, F. Rastegar Nia, J.A. Rueda, N. Sahakyan, Y. Wang, S.S. Xue, Y.F. Yuan, Y.L. Zheng, on behalf of ICRA, ICRANet and USTC team, report: We confirm the results of our previous GCN (Ruffini et al. 2022, GCN 31465). Following the release of the X-ray afterglow (Tohuvavohu et al. 2022, GCN 31347) and the GeV data (Arimoto et al. 2022, GCN 31350) of this source, we can estimate the total (keV+MeV+GeV) isotropic energy (see e.g. Ruffini et al. 2021, MNRAS 504, 5301) to be ~6E54 erg, making this GRB the most powerful GRB in 26 years (a "Petanova"). The period of the new neutron star (see e.g. Ruffini et al. 2021, MNRAS 504, 5301) generating the X-ray afterglow is ~1 ms, the initial mass of the BH (see e.g. Ruffini et al. 2019 ApJ 886, 82) is 6.15 solar mass, the spin parameter is 0.95, and the irreducible mass is 4.98 solar masses (see Fig. 1). The peak of the bolometric flux of supernova is of the order of 1E-17 erg/s/cm^2 and will appear in 73+/-15 days after the GRB trigger, with emissions lasting ~ one month peaking in different infrared bands. The observational follow up of this source is encouraged. Fig. 1: http://www.icranet.org/docs/GRB220101A.pdf
3. Annuncio importante: 80esimo compleanno del Prof. Remo Ruffini (Nizza, 16 - 18 Maggio 2022) e 6° Bego Meeting Summer School (Nizza, 4 - 14 Luglio 2022)
80esimo compleanno del Prof. Remo Ruffini
Siamo felici di invitarVi al 80esimo compleanno del Prof. Remo Ruffini, il giorno 17 Maggio 2022. Le celebrazioni si terranno dal 16 al 18 Maggio presso Villa Ratti, sede dell'ICRANet a Nizza (Francia). L'evento si svolgerà sia in presenza che online. Messaggi di congratulazioni, di auguri e presentazioni scientifiche saranno ben graditi. Il link alla piattaforma Indico sarà annunciato a breve sul sito dell'ICRANet (http://www.icranet.org/). 6° Bego Meeting Summer School Siamo lieti di informarVi che l'ICRANet sta organizzando il "60 Bego Meeting" presso la sede di Villa Ratti, Nizza, dal 4 al 14 Luglio. I temi di questa summer school verteranno sulla distribuzione della materia oscura nell'universo, la fisica del nostro centro galattico, l'estrazione dell'energia da un buco nero rotante tramite la metrica di Kerr, i raggi gamma (GRBs), i nuclei galattici attivi (AGNs), elettrodinamica classica e quantistica, stelle di neutroni, nane bianche, relatività generale e onde gravitazionali. Ogni Vostro contributo su questi temi sarà gradito. La lista dei lecturers, il link alla piattaforma Indico e maggiori dettagli sull'evento saranno resi noti a breve sul sito webdell'ICRANet (http://www.icranet.org/).
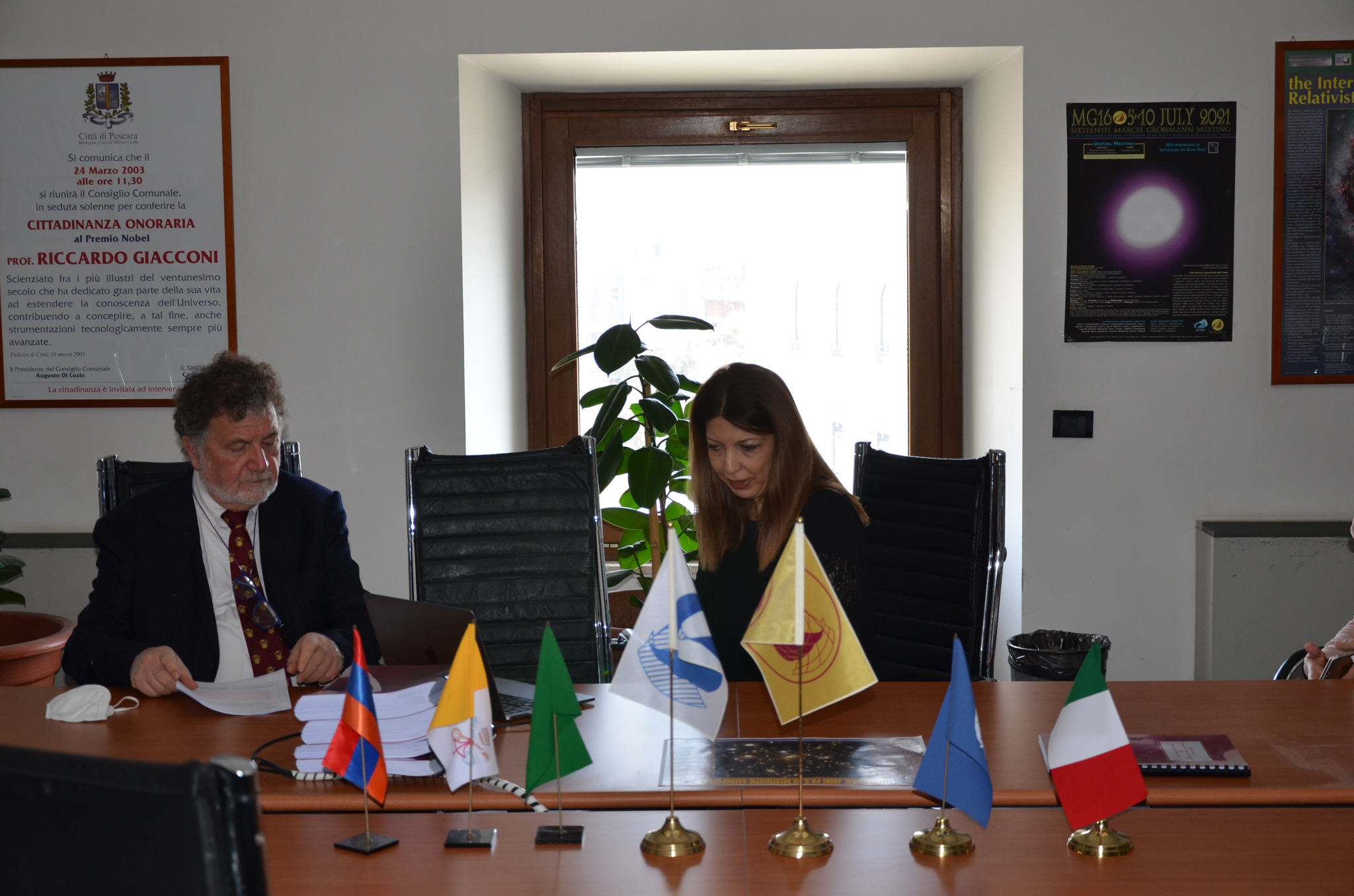
4. Visita di S.E. Tsovinar Hambardzumyan, Ambasciatrice dell'Armenia in Italia, presso il centro ICRANet di Pescara, 16 Marzo 2022
Il 16 Marzo 2022, l'Ambasciatrice Straordinaria e Plenipotenziaria della Repubblica d'Armenia in Italia, S.E. Tsovinar Hambardzumyan e la sua assistente, la Dott.ssa Naira Ghazaryan, hanno visitato il centro ICRANet di Pescara.
Il Prof. Remo Ruffini, Direttore dell'ICRANet, ha mostrato la sede e la sua ricca biblioteca, nella quale sono custoditi libri, fotografie e documenti preziosi. Il Prof. Ruffini ha poi illustrato le attività dell'ICRANet, i principali temi di ricerca e i risultati ottenuti. Inoltre, sono stati presentati i progetti che il centro ICRANet di Pescara sta implementando. Si è infine discusso del ruolo focale dell'ICRANet negli scambi quotidiani di informazioni scientifiche e negli accordi con le principali università ed istituti di ricerca in tutto il mondo.
Il Prof. Narek Sahakyan, Direttore della sede ICRANet in Armenia, ha partecipato virtualmente all'incontro tramite collegamento GoToMeeting. Egli ha evidenziato ancora una volta l'importanza di un centro ICRANet in Armenia, come punto strategico per l'espansione delle adesioni ai Paesi limitrofi. Si è infine ribadita l'importanza della cooperazione scientifica italo-armena nel campo dell'astrofisica relativistica e si è discusso di possibilità future di sviluppo della suddetta cooperazione. Questa notizia è stata pubblicata anche sulla pagina Facebook dell'Ambasciata dell'Armenia in Italia, raggiungibile dal seguente link: https://www.facebook.com/HayastaniDespanutyun/
5. Nuovo accordo di cooperazione tra l'ICRANet e la University of Western Cape (UWC), 1 Marzo 2022
Il 1 Marzo 2022, l'ICRANet ha firmato un nuovo protocollo di cooperazione con la University of Western Cape (UWC) in Sud Africa. I firmatari sono stati il Prof. Tyrone Brian Pretorius (Rettore della UWC), il Prof. Roy Marteens (Prof. di Astronomia & Astrofisica nella UWC), il Prof. Remo Ruffini (Direttore dell'ICRANet) ed il Prof. Narek Sahakyan (Direttore della sede ICRANet in Armenia).
L'accordo resterà valido per 5 anni. Le principali attività congiunte che saranno portate avanti nel quadro del progetto comprendono: la promozione delle attività teoriche e di osservazione nel campo dell'astrofisica relativistica; lo scambio istituzionale di membri, ricercatori, post-doc, e studenti; lo sviluppo di tecnologie e di dati per l'astrofisica su tutte le bande di frequenza; l'organizzazione di corsi, seminari, conferenze, workshops; lo sviluppo di ricerche inter-instituzionali e pubblicazioni congiunte. Per il testo dell'accordo: http://www.icranet.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=1411
6. Nuovo accordo di cooperazione tra l'ICRANet e la Sogang University, 28 Marzo 2022
Il 28 Marzo 2022, l'ICRANet ha firmato un accordo con la Sogang University in Corea del Sud. I firmatari dell'accordo sono stati il Prof. Luke Sim Jong-Hyeok SJ (Presidente della Sogang University), il Prof. Stefano Scopel (Direttore del CQUeST, Sogang University), il Prof. Remo Ruffini (Direttore dell'ICRANet) e dal Prof. Carlo Luciano Bianco (Professore della ICRANet Faculty). L'accordo sarà valido per 5 anni e le principali attività congiunte che saranno portate avanti nel quadro del progetto comprendono: la promozione delle attività teoriche e di osservazione nel campo dell'astrofisica relativistica; lo scambio istituzionale di membri, ricercatori, post-doc, e studenti; lo sviluppo di tecnologie e di dati per l'astrofisica su tutte le bande di frequenza; l'organizzazione di corsi, seminari, conferenze, workshops; lo sviluppo di ricerche inter-instituzionali e pubblicazioni congiunte. Per il testo dell'accordo: http://www.icranet.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=1414
7. Rinnovo dell'accordo di cooperazione tra l'ICRANet e l'Institute of High Energy Physics presso l'Accademia Cinese delle Scienze (IHEP CAS), 7 Marzo 2022
Il 7 Marzo 2022, l'ICRANet e l'Institute of High Energy Physics presso l'Accademia Cinese delle Scienze (IHEP CAS) hanno rinnovato l'accordo di cooperazione. I firmatari sono stati i Prof. Shuang-Nan Zhang (Direttore del Laboratorio della Fisica delle Particelle presso IHEP CAS) ed il Prof. Remo Ruffini (Direttore dell' ICRANet). L'accordo sarà valido per 5 anni e le principali attività congiunte che saranno portate avanti nel quadro del progetto comprendono: la promozione delle attività teoriche e di osservazione nel campo dell'astrofisica relativistica; lo scambio istituzionale di membri, ricercatori, post-doc, e studenti; lo sviluppo di tecnologie e di dati per l'astrofisica su tutte le bande di frequenza; l'organizzazione di corsi, seminari, conferenze, workshops; lo sviluppo di ricerche inter-instituzionali e pubblicazioni congiunte. Per il testo dell'accordo: http://www.icranet.org/ihep
8. Podcast del Prof. Remo Ruffini "20 Marzo 1916: Einstein pubblica la Teoria Generale della relatività", Radio Storia La Repubblica, 20 Marzo 2022
Il 20 Marzo 2022, il canale web Radio Storia di La Repubblica, uno dei maggiori quotidiani in Italia, ha rilasciato un podcast registrato dal Prof. Remo Ruffini, Direttore dell'ICRANet.
Il podcast, dal titolo "20 Marzo 1916: Einstein pubblica la Teoria della Relatività Generale", diretto dal giornalista Francesco De Leo, segue l'evoluzione di eventi storici cruciali, come se fossero appena accaduti. Il podcast del Prof. Ruffini è stato realizzato fingendo di essere nel giorno 20 Marzo 1916, quando Einstein aveva appena pubblicato la teoria della Relatività Generale sugli Annali della Fisica n° 7. In questo articolo, Einstein illustrava l'equazione che indica la forza gravitazionale come una curvatura spazio-tempo. Si tratta di una delle combinazioni più intelligenti di filosofia, intuizione fisica ed abilità matematiche. Il Prof. Ruffini è stato invitato a commentare questo articolo. Il Professore ha ribadito più volte l'importanza e l'influenza di questo lavoro, in cui Einstein riassume e spiega la teoria della relatività, oltre a definirla come una teoria della relatività speciale. Il Prof. Ruffini ci ha inoltre ricordato dell'importanza del contributo scientifico di Hermann Minkowski, il quale riconobbe l'equivalenza formale delle coordinate spazio-temporali e le rese fruibili per l'elaborazione di questa teoria. Einstein ha spiegato il formalismo matematico di Tullio Levi Civita e di Matteo Ricci ed ha finalmente ottenuto l'equazione di campo e della Teoria Generale. Egli ha dimostrato che, se un raggio di luce passa vicino al Sole, lì si potrebbe verificare una deflessione del raggio di luce stesso dovuto alle onde del Sole - ciò avviene anche per un segnale luce che passa vicino ad un pianeta. Questa visione modifica totalmente la fisica tradizionale Newtoniana, secondo la quale un raggio di luce si propaga in modo lineare. Einstein inoltre si aspettava che la luce originata da una stella modifica la frequenza del suo movimento partendo dalla stella stessa, indicando uno shift verso lunghezze d'onda più lunghe. Questo è un altro concetto che si distacca dalla teoria di Newton. In aggiunta, ai tempi di Newton e Keplero, l'astronomia classica concepiva il movimento come in ellissi; Einstein nel 1916 sosteneva la presenza di una piccola quantità che modificava questo movimento, prevedendo così il moto "a rosetta" di 43 secondi d'arco per secolo: si tratta di una piccola grandezza, ma è concettualmente rivoluzionaria. Nel commento all'articolo di Einstein, il Prof. Ruffini ha spiegato che, come affermava anche Einstein stesso, il tempo non esiste, ma bensì ci sono tre componenti spaziali e una temporale che lavorano insieme, come predetto anche da Minkowski. Pertanto, da allora, la fisica non è stata più vista come una teoria di uno o tre componenti, bensì come una teoria composta dall'interazione di quattro dimensioni. Einstein sosteneva che non ci fosse solo il tempo, ma lo spazio - tempo, descritto dalla metrica di Tullio Levi Civita e Matteo Ricci: tutto questo rappresentava una rivoluzione concettuale e dava origine ad una nuova fisica, a nuove osservazioni e ad una nuova conoscenza. Per ascoltare il podcast (in italiano): https://www.repubblica.it/podcast/storie/radio-storia/stagione1/
9. Pubblicazioni recenti
Rueda, J. A.; Ruffini, R.; Kerr, R. P., Gravitomagnetic interaction of a Kerr black hole with a magnetic field as the source of the jetted GeV radiation of gamma-ray bursts, The Astrophysical Journal; in press.
We show that the gravitomagnetic interaction of a Kerr black hole (BH) with a surrounding magnetic field induces an electric field that accelerates charged particles to ultra-relativistic energies in the vicinity of the BH. Along the BH rotation axis, these electrons/protons can reach energies of even thousands of PeV, so stellar-mass BHs in long gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) and supermassive BHs in active galactic nuclei (AGN) can contribute to the ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) thorough this mechanism. At off-axis latitudes, the particles accelerate to energies of hundreds of GeV and emit synchrotron radiation at GeV energies. This process occurs within 60° around the BH rotation axis, and due to the equatorial-symmetry, it forms a double-cone emission. We outline the theoretical framework describing these acceleration and radiation processes, how they extract the rotational energy of the Kerr BH and the consequences for the astrophysics of GRBs. Link al preprint: https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.03471 C. R. Argüelles, E. A. Becerra-Vergara, A. Krut, R. Yunis, J. A. Rueda and R. Ruffini, Reshaping our understanding on structure formation with the quantum nature of the dark matter, published on International Journal of Modern Physics D Vol. 31, No. 02, 2230002 (2022). We study the nonlinear structure formation in cosmology accounting for the quantum nature of the dark matter (DM) particles in the initial conditions at decoupling, as well as in the relaxation and stability of the DM halos. Different from cosmological N-body simulations, we use a thermodynamic approach for collisionless systems of self-gravitating fermions in general relativity, in which the halos reach the steady state by maximizing a coarse-grained entropy. We show the ability of this approach to provide answers to crucial open problems in cosmology, among others: the mass and nature of the DM particle, the formation and nature of supermassive black holes in the early Universe, the nature of the intermediate mass black holes in small halos, and the core-cusp problem. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218271822300026 Gregory Vereshchagin, Liang Li, Damien Bégué, Is magnetically dominated outflow required to explain GRBs?, published on Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, stac757, on March 22, 2022. The composition of relativistic outflows producing gamma-ray bursts is a long standing open question. One of the main arguments in favour of magnetically dominated outflows is the absence of photospheric component in their broadband time resolved spectra, with such notable example as GRB 080916C. Here, we perform a time-resolved analysis of this burst and confirm the previous detection of an additional spectral component. We show that this subdominant component is consistent with the photosphere of ultrarelativistic baryonic outflow, deep in the coasting regime. We argue that, contrary to previous statements, the magnetic dominance of the outflow is not required for the interpretation of this GRB. Moreover, simultaneous detection of high energy emission in its prompt phase requires departure from a one-zone emission model. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stac757 MAGIC collaboration, Combined searches for dark matter in dwarf spheroidal galaxies observed with the MAGIC telescopes, including new data from Coma Berenices and Draco, published in Physics of the Dark Universe, Volume 35, March 2022, 100912. Milky Way dwarf spheroidal galaxies (dSphs) are among the best candidates to search for signals of dark matter annihilation with Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes, given their high mass-to-light ratios and the fact that they are free of astrophysical gamma-ray emitting sources. Since 2011, MAGIC has performed a multi-year observation program in search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) in dSphs. Results on the observations of Segue 1 and Ursa Major II dSphs have already been published and include some of the most stringent upper limits (ULs) on the velocity-averaged cross-section σann v of WIMP annihilation from observations of dSphs. In this work, we report on the analyses of 52.1 h of data of Draco dSph and 49.5 h of Coma Berenices dSph observed with the MAGIC telescopes in 2018 and in 2019 respectively. No hint of a signal has been detected from either of these targets and new constraints on the σann v of WIMP candidates have been derived. In order to improve the sensitivity of the search and reduce the effect of the systematic uncertainties due to the -factor estimates, we have combined the data of all dSphs observed with the MAGIC telescopes. Using 354.3 h of dSphs good quality data, 95% CL ULs on σann v have been obtained for 9 annihilation channels. For most of the channels, these results reach values of the order of 10-24 cm3/s at ∼ 1 TeV and are the most stringent limits obtained with the MAGIC telescopes so far. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dark.2021.100912 MAGIC collaboration, Investigating the Blazar TXS 0506+056 through Sharp Multiwavelength Eyes During 2017-2019, published on The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 927, Issue 2, id.197. The blazar TXS 0506+056 got into the spotlight of the astrophysical community in 2017 September, when a high-energy neutrino detected by IceCube (IceCube-170922A) was associated at the 3σ level with a γ-ray flare from this source. This multi-messenger photon-neutrino association remains, as per today, the most significant association ever observed. TXS 0506+056 was a poorly studied object before the IceCube-170922A event. To better characterize its broadband emission, we organized a multiwavelength campaign lasting 16 months (2017 November to 2019 February), covering the radio band (Metsähovi, OVRO), the optical/UV (ASAS-SN, KVA, REM, Swift/UVOT), the X-rays (Swift/XRT, NuSTAR), the high-energy γ rays (Fermi/LAT), and the very high-energy (VHE) γ rays (MAGIC). In γ rays, the behavior of the source was significantly different from the behavior in 2017: MAGIC observations show the presence of flaring activity during 2018 December, while the source only shows an excess at the 4σ level during the rest of the campaign (74 hr of accumulated exposure); Fermi/LAT observations show several short (on a timescale of days to a week) flares, different from the long-term brightening of 2017. No significant flares are detected at lower energies. The radio light curve shows an increasing flux trend that is not seen in other wavelengths. We model the multiwavelength spectral energy distributions in a lepto-hadronic scenario, in which the hadronic emission emerges as Bethe-Heitler and pion-decay cascade in the X-rays and VHE γ rays. According to the model presented here, the 2018 December γ-ray flare was connected to a neutrino emission that was too brief and not bright enough to be detected by current neutrino instruments. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/ac531d MAGIC collaboration, Multiwavelength study of the gravitationally lensed blazar QSO B0218+357 between 2016 and 2020, published on Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 510, Issue 2. We report multiwavelength observations of the gravitationally lensed blazar QSO B0218+357 in 2016-2020. Optical, X-ray, and GeV flares were detected. The contemporaneous MAGIC observations do not show significant very high energy (VHE; ≳100 GeV) gamma-ray emission. The lack of enhancement in radio emission measured by The Owens Valley Radio Observatory indicates the multizone nature of the emission from this object. We constrain the VHE duty cycle of the source to be <16 2014-like flares per year (95 per cent confidence). For the first time for this source, a broad-band low-state spectral energy distribution is constructed with a deep exposure up to the VHE range. A flux upper limit on the low-state VHE gamma-ray emission of an order of magnitude below that of the 2014 flare is determined. The X-ray data are used to fit the column density of (8.10 ± 0.93stat) × 1021 cm-2 of the dust in the lensing galaxy. VLBI observations show a clear radio core and jet components in both lensed images, yet no significant movement of the components is seen. The radio measurements are used to model the source-lens-observer geometry and determine the magnifications and time delays for both components. The quiescent emission is modelled with the high-energy bump explained as a combination of synchrotron-self-Compton and external Compton emission from a region located outside of the broad-line region. The bulk of the low-energy emission is explained as originating from a tens-of-parsecs scale jet. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stab3454 Behzad Eslam Panah, and Khadijie Jafarzade, Thermal stability, P−V criticality and heat engine of charged rotating accelerating black holes, General Relativity and Gravitation. 54 (2022) 19 In this paper, we study thermodynamic features of the charged rotating accelerating black holes in anti-de Sitter spacetime. First, we consider these black holes as the thermodynamic systems and analyze thermal stability/instability through the use of heat capacity in the canonical ensemble. We also investigate the effects of angular momentum, electric charge and string tension on the thermodynamic quantities and stability of the system. Considering the known relation between pressure and the cosmological constant, we extract the critical quantities and discuss how the mentioned parameters affect them. Then, we construct a heat engine by taking into account this black hole as the working substance, and obtain the heat engine efficiency by considering a rectangle heat cycle in the P−V plane. We examine the effects of black hole parameters on the efficiency and analyze their effective roles. Finally, by comparing the engine efficiency with Carnot efficiency, we investigate conditions in order to have a consistent thermodynamic second law. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-022-02904-9 Tayyebeh Yazdizadeh, Gholam Hossein Bordbar, and Behzad Eslam Panah, The structure of hybrid neutron star in Einstein-Λ gravity, Physics of the Dark Universe 35 (2022) 100982. In this paper, we investigate the structure of neutron stars by considering both the effects of the cosmological constant and the existence of quark matter for neutron stars in Einstein's gravity. For this purpose, we use a suitable equation of state (EoS) which includes a layer of hadronic matter, a mixed phase of quarks and hadrons, and a quark matter in the core. To investigate the effect of the cosmological constant on the structure of hybrid neutron stars, we utilize the modified TOV equation in Einstein -Λ gravity. Then we derive the mass-radius relation for different values of the cosmological constant. Our results show that for small values of the cosmological constant (Λ), especially for the cosmological constant from the cosmological perspective (Λ=10−52m−2),Λ has no significant effect on the structure of hybrid neutron stars. But for higher values, for example, by considering Λ>10−14 m−2, this quantity affects the maximum mass and radius of these stars. We find an upper limit for the cosmological constant as Λ<9×10−13m−2, based on the fact that the gravitational redshift cannot be more than 1 for stars. The maximum mass and radius of these stars decrease by increasing the cosmological constant Λ. Also, by determining and analyzing radius, the compactness, Kretschmann scalar, and gravitational red shift of the hybrid neutron stars with M=1.4M⊙ in the presence of the cosmological constant, we find that by increasing Λ, they are contracted. Also, our results for dynamical stability show that these stars satisfy this condition. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dark.2022.100982 |
|||||||
|
||