
| Newsletter Italian December 2020/January 2021 |

|

|





ICRANet Newsletter
2014 -
2015 -
2016
2017 - 2018 - 2019 2020 February/March - April/May - June/July - August/September - October/November - December/January 2021 2021 - 2022
ICRANet Newsletter
Dicembre 2020 - Gennaio 2021
SOMMARIO
1. Shedding new light on sterile neutrinos from XENON1T experiment 2. Nuovo Accordo di cooperazione scientifica tra la USTC e l'ICRANet, 28 Dicembre 2020 3. Nuovo Accordo di cooperazione tra CIMPA e ICRANet, 20 Gennaio 2021 4. "L'eclissi di sole e la misura del diametro solare", meeting online, 14 Dicembre 2020 5. "Congiunzione solstizio tra storia e meccanica celeste", meeting online, 21 Dicembre 2020 e comunicato stampa ICRANet sull'evento 6. Pubblicazioni recenti
1. Shedding new light on sterile neutrinos from XENON1T experiment
A new paper co-authored by Shakeri, S., Hajkarim, F. & Xue, SS. has been published on December 30, 2020 in Journal of High Energy Physics.
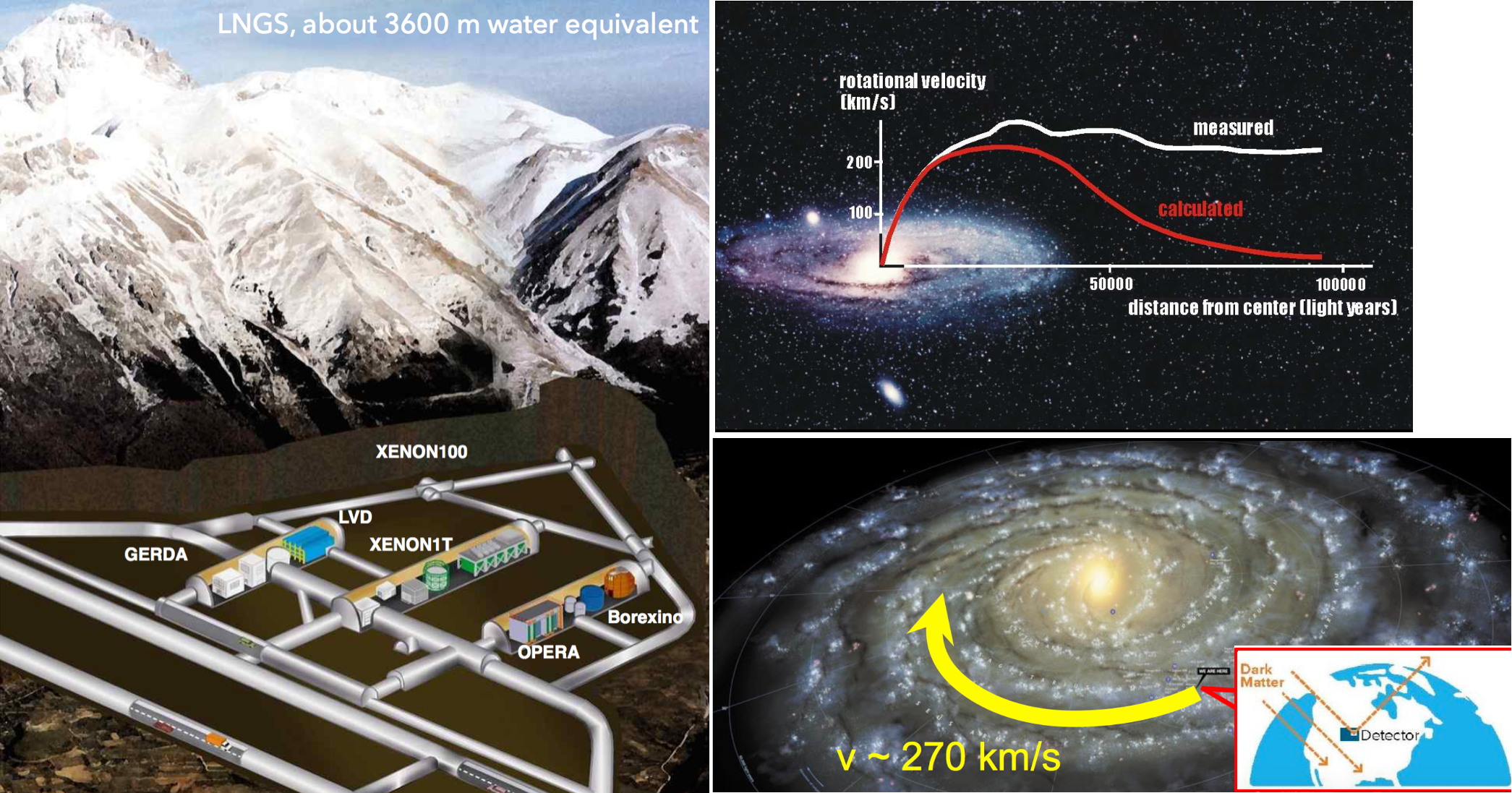
Fig. 1, 2 and 3: XENON1T experiment at INFN Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso. 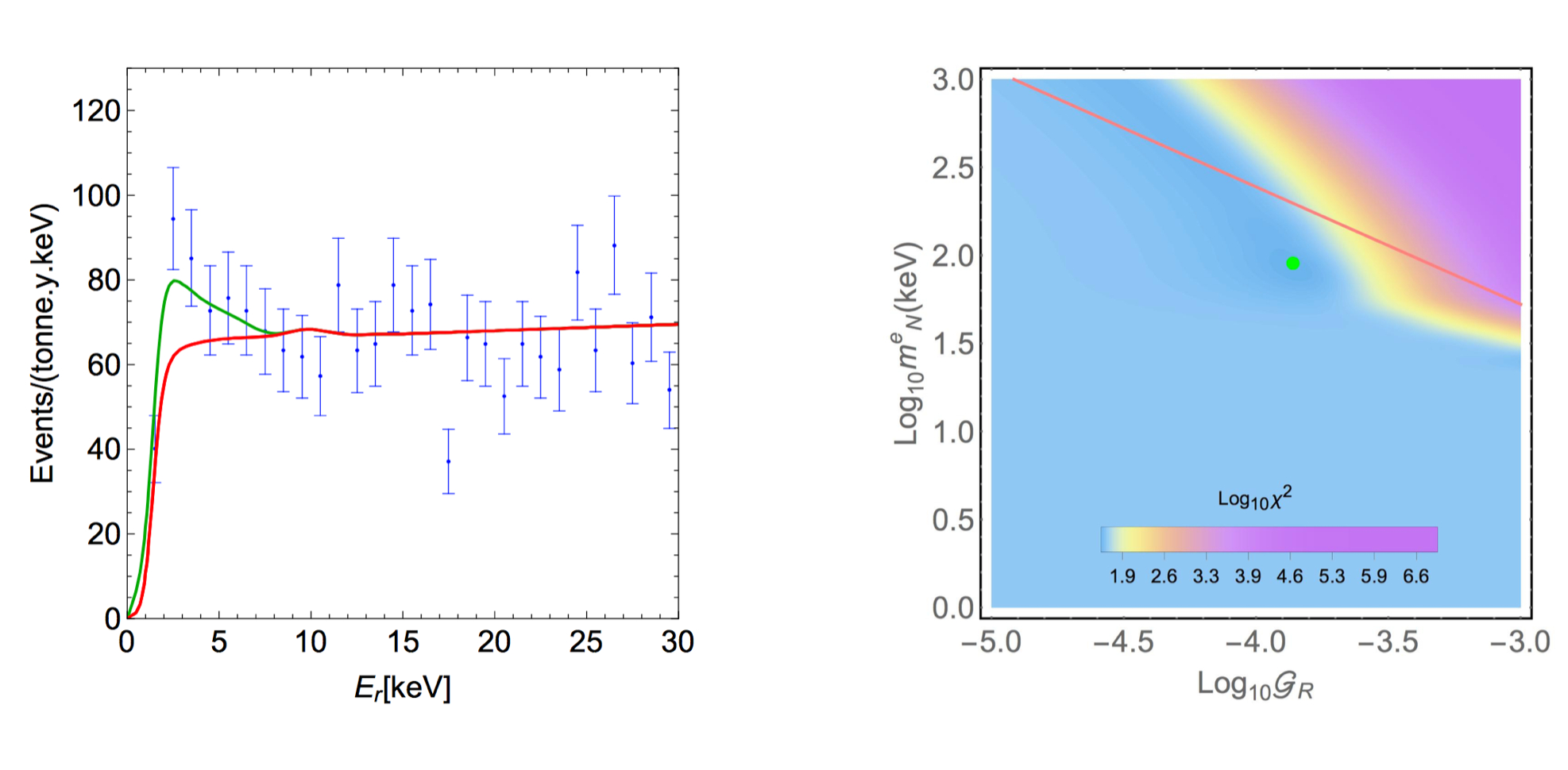
Fig. 4 and 5: In the left panel events versus recoil energy including the error bars are shown in blue color. The solid red line is the background model computed by XENON Collaboration. The additional recoil due to the sterile neutrino DM interaction with the Xenon electrons are shown by green solid curve. Right panel shows best fit points for the coupling and mass of electron sterile neutrino. The XENON1T collaboration recently reported the excess of events from recoil electrons which may be sign of a fundamental new discovery about our universe. The XENON1T as the world's most sensitive dark matter experiment hosted in an underground laboratory beneath a mountain at Gran Sasso National Laboratory (INFN Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso) in Italy. The evidence for the existence of dark matter (DM) which makes up 85% of the matter in the universe, is implied from various astrophysical and cosmological observations, but scientists still do not know the particle nature of this exotic material. A group of scientists She-sheng Xue from ICRANet/ICRA, Soroush Shakeri from ICRANet-Isfahan and Isfahan University of Technology (IUT) and Fazlollah Hajkarim from Università degli Studi di Padova and Goethe Universität, claimed to have found a new interpretation for XENON1T excess by considering effective interactions between the DM sterile neutrinos and the SM particles. Sterile neutrinos as a warm DM with masses at keV scale are well motivated from astrophysical and cosmological point of view. It is shown that sterile neutrinos with masses around 90 keV and specific effective coupling can fit well with the XENON1T data where the best fit points preserving DM constraints and possibly describe the anomalies in other experiments. In addition to explain XENON1T anomaly, the scenario presented in this group has some distinctive features which can be used to distinguish between their scenario and other beyond SM proposals. This research, as shown by the references below, has been well developed for many years in ICRANet to understand the nature of dark matter particles as a fermion with the mass in keV range. It has been individuated the window 50-350 keV for the mass of fermionic dark matter ("ino") from the analysis of the rotation curves of the Milky Way. Accurate analysis has been done by ICRANet member in the case of the S2 and G2 orbits around the Galactic center and explained them with the distribution of DM for 56 keV fermions. The XENON1T new results attract so much attention in Physics community. Physicists will likely treat the XENON1T results as preliminary for the near future. An upcoming, larger XENON experiment called XENONnt, still under construction in Italy besides the next generation of XENON detectors may shed light on the dark matter nature and low energy neutrino physic beyond SM. • XENON collaboration, Excess electronic recoil events in XENON1T, Phys. Rev. D 102(2020) 072004 • Soroush Shakeri, Fazlollah Hajkarim, She-Sheng Xue, Shedding New Light on Sterile Neutrinos from XENON1T Experiment, JHEP12(2020)194 • C.R. Argüelles, N.E. Mavromatos, J.A. Rueda and R. Ruffini, The role of self-interacting right-handed neutrinos in galactic structure, JCAP 04 (2016) 038 • N. E. Mavromatos, C. R. Argüelles, R. Ruffini, J. A. Rueda, Self- interacting dark matter, International Journal of Modern Physics D 26 (2017) 1730007 • R. Ruffini, C. R. Argüelles, J. A. Rueda, On the core-halo distribution of dark matter in galaxies, MNRAS 451 (2015) 622-628 • E. A. Becerra-Vergara, C. R. Argüelles, A. Krut, J. A. Rueda, R. Ruffini, The geodesic motion of S2 and G2 as a test of the fermion dark matter constituency of our galactic core, A&A 641, A34 (2020) • R. Yunis, C. R. Argüelles, N. E. Mavromatos, A. Moliné, A. Krut, M. Carinci, J. A. Rueda, R. Ruffini, Galactic center constraints on self-interacting sterile neutrinos from fermionic dark matter ("ino") models, Physics of the Dark Universe 30 (2020) 100699 Link to the paper https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP12(2020)194
2. Nuovo Accordo di cooperazione scientifica tra la USTC e l'ICRANet, 28 Dicembre 2020
Il 28 Dicembre 2020 è stato firmato un accordo di cooperazione scientifica tra l'ICRANet e la University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) dal Prof. Xinhe Bao (Presidente USTC) e dal Prof. Remo Ruffini (Direttore ICRANet). Le principali attività congiunte che saranno portate avanti nel quadro del progetto comprendono: la promozione di attività teoriche e pratiche nel campo dell'Astrofisica Relativistica; la collaborazione tra membri della Faculty, ricercatori, Dottorandi e studenti; l'organizzazione di corsi di insegnamento e ricerca, di seminari, conferenze, workshops, e il lavoro congiunto per le pubblicazioni scientifiche. L'accordo sarà valido per 5 anni. Per il testo dell'accordo: http://www.icranet.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=1353
3. Nuovo Accordo di cooperazione tra CIMPA e ICRANet, 20 Gennaio 2021
Il 20 Gennaio 2021 è stato firmato un nuovo accord di cooperazione tra l'ICRANet e il Centre International de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées (CIMPA) dal Prof. Barry Green (Presidente CIMPA), dal Prof. Christophe Ritzenthaler (Direttore Esecutivo CIMPA), dal Prof. Remo Ruffini (Direttore ICRANet) e dal Prof. Jorge A. Rueda H. (Professore della Faculty ICRANet). Le principali attività congiunte che saranno portate avanti nel quadro del progetto comprendono: la promozione di attività teoriche e pratiche nel campo dell'Astrofisica Relativistica; la collaborazione tra membri della Faculty, ricercatori, Dottorandi e studenti; l'organizzazione di corsi di insegnamento e ricerca, di seminari, conferenze, workshops, e il lavoro congiunto per le pubblicazioni scientifiche. L'accordo sarà valido per 5 anni. Per il testo dell'accordo: http://www.icranet.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=1354.
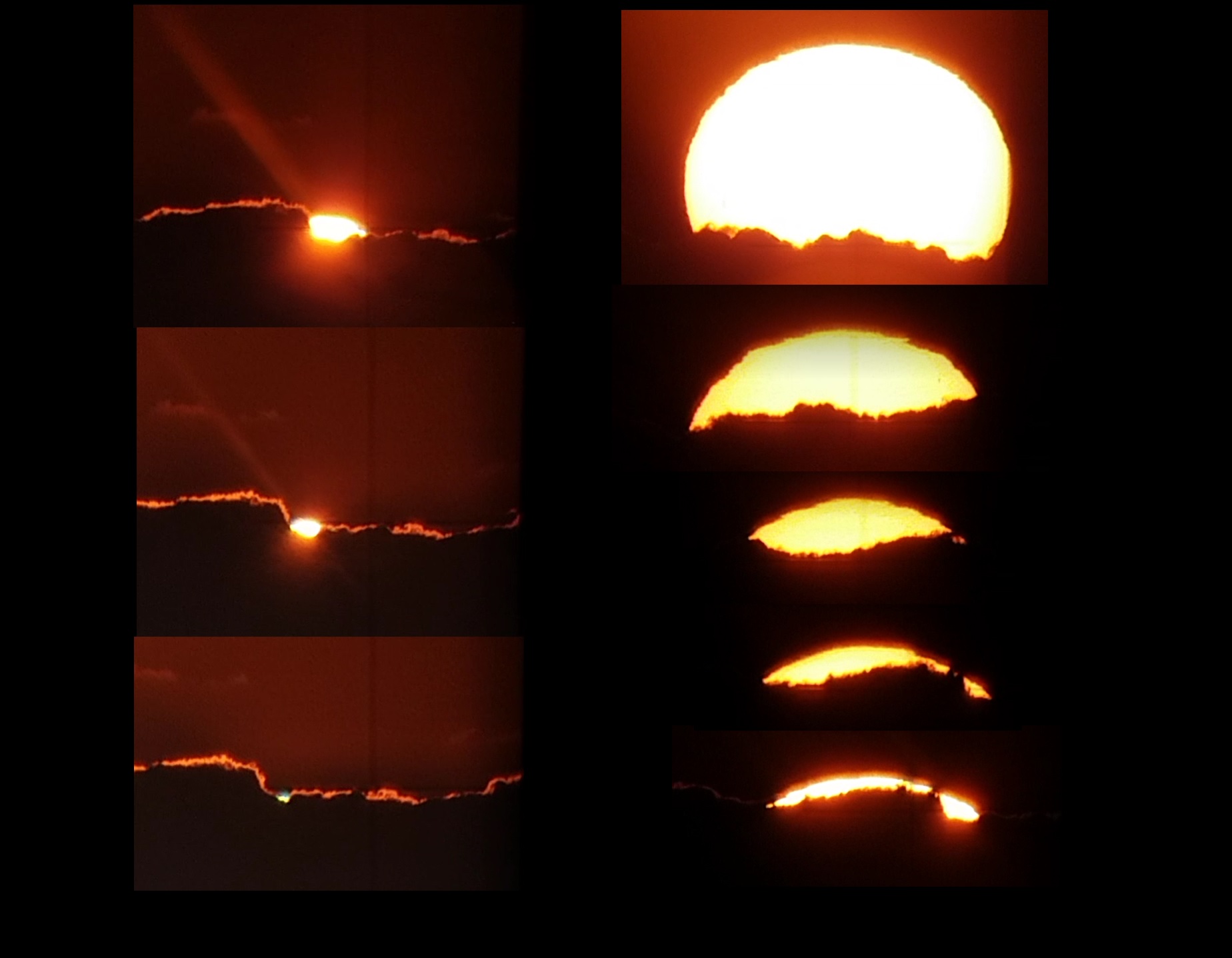
4. "L'eclissi di sole e la misura del diametro solare", meeting online, 14 Dicembre 2020
L'evento "L'eclissi di sole e la misura del diametro solare. Cacciatori di eclissi dal 1500 ad oggi: Cristoforo Clavio, Halley, padre Secchi, Eddington e lo stato dell'arte oggi" si è svolto virtualmente il 14 Dicembre 2020. Il Prof. Costantino Sigismondi, collaboratore ICRANet e chair del meeting, grazie alla collaborazione con l'ICRANet e con molteplici scienziati da tutto il mondo, ha organizzato questo meeting virtuale e un podcast meeting per creare una piacevole occasione di discussione e confronto tra studenti e ricercatori. Il meeting online è iniziato alle h 16:30 di Lunedì 14 Dicembre con i saluti di apertura del Prof. Sigismondi per poi proseguire con presentazioni su "Eclissi e fisica solare a Torino" da parte del Prof. Alessandro Bemporad (INAF – Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino, Italia), su "Gli studi sulla Fisica e sul Sole all'Università di Roma Tor Vergata" e su "Il lascito di Angelo Secchi: Studio della connessione Sole-Terra" da parte del Prof. Francesco Berrilli (Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma Tor Vergata - Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei), sul "Diametro del sole misurato dalle osservazioni delle eclissi" da parte del Prof. Andrea Raponi (INAF IAPS), sul Telescopio Copernico in Cima Ekar (un Telescopio INFN situato presso l'Osservatorio Astronomico di Asiago) da parte del Prof. Paolo Ochner e del Prof. Armando Sorrenti (Università di Padova), su "Halley" da parte del Prof. Giuseppe Massara (Università La Sapienza di Roma) e sul "Punto nave" da parte del Prof. Cosimo Palagiano (Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei). Alla fine di queste presentazioni, il Prof. Sigismondi ha mostrato e spiegato nel dettaglio alcuni video live di eclissi solari osservate dall'Argentina, dal Cile, dall'Egitto e dal Paraguay. L'ultima parte dell'evento è stata dedicata ai saluti conclusive da parte del Prof. Remo Ruffini, Direttore ICRANet. Questa sezione teorica del meeting è stata integrata con del material podcast preparato dal Prof. Sigismondi, dal Prof. Berilli e dal Prof. Ramponi, disponibile sulla pagina web del meeting. Il programma dell'evento e tutti i materiali del podcast sono disponibili al seguente link: http://www.icranet.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=1348
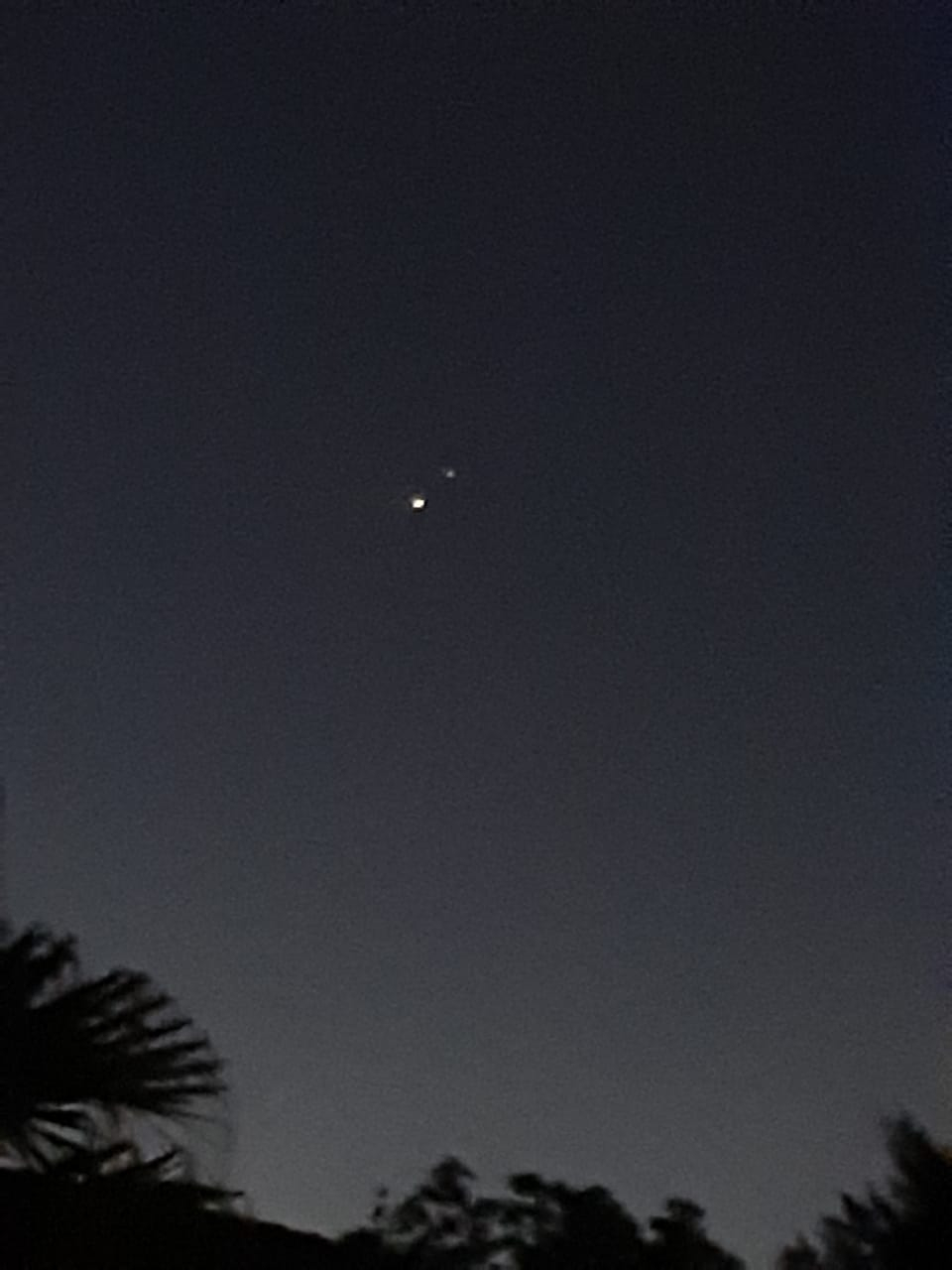
5. "Congiunzione solstizio tra storia e meccanica celeste", meeting online, 21 Dicembre 2020e comunicato stampa ICRANet sull'evento
L'evento "Congiunzione solstizio tra storia e meccanica celeste. Come le congiunzioni planetarie sono state le fonti per implementare le teorie planetarie" si è svolto online il 21 Dicembre 2020, in occasione della grande congiunzione tra Giove e Saturno. Questo ci ha permesso di ragionare sull'ipotesi formulate da Keplero sulla Stella di Betlemme: secondo lui la congiunzione analoga del 7/6 a. c. fu la causa dell'apparizione della stella, non era la stella.
Il Prof. Costantino Sigismondi, collaboratore ICRANet e chair del meeting, grazie alla collaborazione con l'ICRANet e con molteplici scienziati da tutto il mondo, ha organizzato questo meeting virtuale e un podcast meeting per creare una piacevole occasione di discussione e confronto tra studenti e ricercatori. Il meeting online è iniziato alle 16:30 di Lunedì 21 Dicembre, con i saluti di aperture da parte del Prof. Sigismondi per poi proseguire con presentazioni su "Breve storia e attività dello IOTA/ES" da parte del Prof. Konrad Guhl (IOTA), su "Congiunzioni e occultazioni" da parte del Prof. Paolo Ochner (Università di Padova), su "Keplero e la grande congiunzione" da parte della Prof.ssa Anna Maria Lombardi (Università di Milano) e sulle"Congiunzioni planetarie, disuguaglianze invarianti e sulle oscillazioni solari-climatiche" da parte del Prof. Nicola Scafetta (Università di Napoli). I saluti conclusive sono stati fatti dal Prof. Rahim Moradi (Professore della Faculty ICRANet) per conto del Prof. Remo Ruffini (Direttore ICRANet). Questa sezione teorica del meeting è stata integrata con del material podcast preparato dal Prof. Sigismondi (su "Giove, Saturno, Urano e Nettuno 1821", sul "Transito Meridiano a San Pietro 16 Dicembre", su "Giove e Marte nel 1591", su "Giove e Saturno" sia nel 1563 che nel 7/6 d. C., su "L'Astronomia nei Vangeli - Stella di Betlemme ed eclissi del Venerdì Santo"). Altro materiale è stato preparato dal Prof. Pascal Descamps (sul "riavvicinamento Giove-Saturno 7 a.c.", sul "riavvicinamento Giove-Saturno nel 1562", sui "riavvicinamenti Marte-Giove nel 1591" e sui "riavvicinamenti Marte-Saturno nel 1604"), dal Prof. Paolo Zanna (su "La congiunzione tra noi"), dal Prof. Giorgio Rossi (sulla "Congiunzione Giove-Saturno nel 1563"), dal Prof. Marco Di Capua e dalla Prof.ssa Elizabeth Stillwachs - Marina Green, San Francisco, California USA (con alcune foto di Giove e Saturno visti da San Francisco), dal Prof. Enrico Guliani e dal Prof. Paul Waddington (sulla "Congiunzione Giove-Saturno" e sulla "Luna del solstizio d'inverno"). Il programma dell'evento e tutti i materiali del podcast sono disponibili al seguente link: http://www.icranet.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=1351
In questa occasione, il Prof. Sigismondi e lo staff dell'ICRANet hanno preparato anche un comunicato stampa, sia in italiano che in inglese.
6. Pubblicazioni recenti
Shakeri, S., Hajkarim, F. & Xue, SS. Shedding new light on sterile neutrinos from XENON1T experiment, published in J. High Energ. Phys. 2020, 194 (2020).
The XENON1T collaboration recently reported the excess of events from recoil electrons, possibly giving an insight into new area beyond the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics. We try to explain this excess by considering effective interactions between the sterile neutrinos and the SM particles. In this paper, we present an effective model based on one-particle-irreducible interaction vertices at low energies that are induced from the SM gauge symmetric four-fermion operators at high energies. The effective interaction strength is constrained by the SM precision measurements, astrophysical and cosmological observations. We introduce a novel effective electromagnetic interaction between sterile neutrinos and SM neutrinos, which can successfully explain the XENON1T event rate through inelastic scattering of the sterile neutrino dark matter from Xenon electrons. We find that sterile neutrinos with masses around 90 keV and specific effective coupling can fit well with the XENON1T data where the best fit points preserving DM constraints and possibly describe the anomalies in other experiments. Link: https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP12(2020)194 R. Yunis, C. R. Argüelles, N. E. Mavromatos, A. Moliné, A. Krut, M. Carinci, J. A. Rueda, R. Ruffini, Galactic center constraints on self-interacting sterile neutrinos from fermionic dark matter ("ino") models, published in Physics of the Dark Universe, Volume 30, article id. 100699 on December 2020. The neutrino minimal standard model (νMSM) has been tightly constrained in the recent years, either from dark matter (DM) production or from X-ray and small-scale observations. However, current bounds on sterile neutrino DM can be significantly modified when considering a vMSM extension, in which the DM candidates interact via a massive (axial) vector field. In particular, standard production mechanisms in the early Universe can be affected through the decay of such a massive mediator. We perform an indirect detection analysis to study how the vMSM parameter-space constraints are affected by said interactions. We compute the X-ray fluxes considering a DM profile that self-consistently accounts for the particle physics model by using an updated version of the Ruffini-Argüelles-Rueda (RAR) fermionic ("ino") model, instead of phenomenological profiles such as the Navarro-Frenk-White (NFW) distribution. We show that the RAR profile accounting for interacting DM, is compatible with measurements of the Galaxy rotation curve and constraints on the DM self-interacting cross section from the Bullet cluster. A new analysis of the X-ray NuSTAR data in the central parsec of the Milky Way, is here performed to derive constraints on the self-interacting sterile neutrino parameter-space. Such constraints are stronger than those obtained with commonly used DM profiles, due to the dense DM core characteristic of the RAR profiles. Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S221268641930370X?via%3Dihub Link nasa-ads: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020PDU....3000699Y/abstract J. D. Uribe, E. A. Becerra-Vergara, J. A. Rueda, Neutrino Oscillations in Neutrino-Dominated Accretion Around Rotating Black Holes, published in Universe, vol. 7, issue 1, p. 7 on January 2021. In the binary-driven hypernova model of long gamma-ray bursts, a carbon-oxygen star explodes as a supernova in the presence of a neutron star binary companion in close orbit. Hypercritical (i.e., highly super-Eddington) accretion of the ejecta matter onto the neutron star sets in, making it reach the critical mass with consequent formation of a Kerr black hole. We have recently shown that, during the accretion process onto the neutron star, fast neutrino flavor oscillations occur. Numerical simulations of the above system show that a part of the ejecta stays bound to the newborn Kerr black hole, leading to a new process of hypercritical accretion. We address herein, also for this phase of the binary-driven hypernova, the occurrence of neutrino flavor oscillations given the extreme conditions of high density (up to 1012 g cm−3) and temperatures (up to tens of MeV) inside this disk. We estimate the behavior of the electronic and non-electronic neutrino content within the two-flavor formalism (νeνx) under the action of neutrino collective effects by neutrino self-interactions. We find that in the case of inverted mass hierarchy, neutrino oscillations inside the disk have frequencies between ∼(105-109) s−1, leading the disk to achieve flavor equipartition. This implies that the energy deposition rate by neutrino annihilation (ν+ν¯→e−+e+) in the vicinity of the Kerr black hole is smaller than previous estimates in the literature not accounting for flavor oscillations inside the disk. The exact value of the reduction factor depends on the νe and νx optical depths but it can be as high as ∼5. The results of this work are a first step toward the analysis of neutrino oscillations in a novel astrophysical context, and as such, deserve further attention. Link: https://www.mdpi.com/2218-1997/7/1/7 Link nasa-ads: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021Univ....7....7U/abstract Sahakyan, N.; Giommi, P., The strange case of the transient HBL blazar 4FGL J1544.3-0649, published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 202, stab011. We present a multifrequency study of the transient γ-ray source 4FGL J1544.3-0649, a blazar that exhibited a remarkable behavior raising from the state of an anonymous mid-intensity radio source, never detected at high energies, to that of one of the brightest extreme blazars in the X-ray and γ-ray sky. Our analysis shows that the averaged γ-ray spectrum is well described by a powerlaw with a photon index of 1.87 ± 0.04, while the flux above 100 MeV is (8.0 ± 0.9) × 10-9 photon cm-2 s-1, which increases during the active state of the source. The X-ray flux and spectral slope are both highly variable, with the highest 2-10 keV flux reaching (1.28 ± 0.05) × 10-10 erg cm-2 s-1. On several observations the X-ray spectrum hardened to the point implying as SED peak moving to energies larger than 10 keV. As in many extreme blazars the broadband spectral energy distribution can be described by a homogeneous one-zone synchrotron-self-Compton leptonic model. We briefly discuss the potential implications for high-energy multi-messenger astrophysics in case the dual behavior shown by 4FGL J1544.3-0649 does not represent an isolated case, but rather a manifestation of a so far unnoticed relatively common phenomenon. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stab011 Link: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021MNRAS.tmp...56S/abstract Acciari, V. A.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L. A..... Sahakyan, N., et al., Multiwavelength variability and correlation studies of Mrk 421 during historically low X-ray and γ-ray activity in 2015-2016, published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2020, staa3727. We report a characterization of the multi-band flux variability and correlations of the nearby (z=0.031) blazar Markarian 421 (Mrk 421) using data from Metsähovi, Swift, Fermi-LAT, MAGIC, FACT and other collaborations and instruments from November 2014 till June 2016. Mrk 421 did not show any prominent flaring activity, but exhibited periods of historically low activity above 1 TeV (F>1TeV < 1.7× 10-12 ph cm-2 s-1) and in the 2-10 keV (X-ray) band (F2 - 10 keV < 3.6 × 10-11 erg cm-2 s-1), during which the Swift-BAT data suggests an additional spectral component beyond the regular synchrotron emission. The highest flux variability occurs in X-rays and very-high-energy (E>0.1 TeV) γ-rays, which, despite the low activity, show a significant positive correlation with no time lag. The HRkeV and HRTeV show the harder-when-brighter trend observed in many blazars, but the trend flattens at the highest fluxes, which suggests a change in the processes dominating the blazar variability. Enlarging our data set with data from years 2007 to 2014, we measured a positive correlation between the optical and the GeV emission over a range of about 60 days centered at time lag zero, and a positive correlation between the optical/GeV and the radio emission over a range of about 60 days centered at a time lag of 43+9−6 days. This observation is consistent with the radio-bright zone being located about 0.2 parsec downstream from the optical/GeV emission regions of the jet. The flux distributions are better described with a LogNormal function in most of the energy bands probed, indicating that the variability in Mrk 421 is likely produced by a multiplicative process. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/staa3727 Link: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020MNRAS.tmp.3563A/abstract |
|||||
|
||





